Understanding Respiratory Diseases: Causes, Symptoms and Management
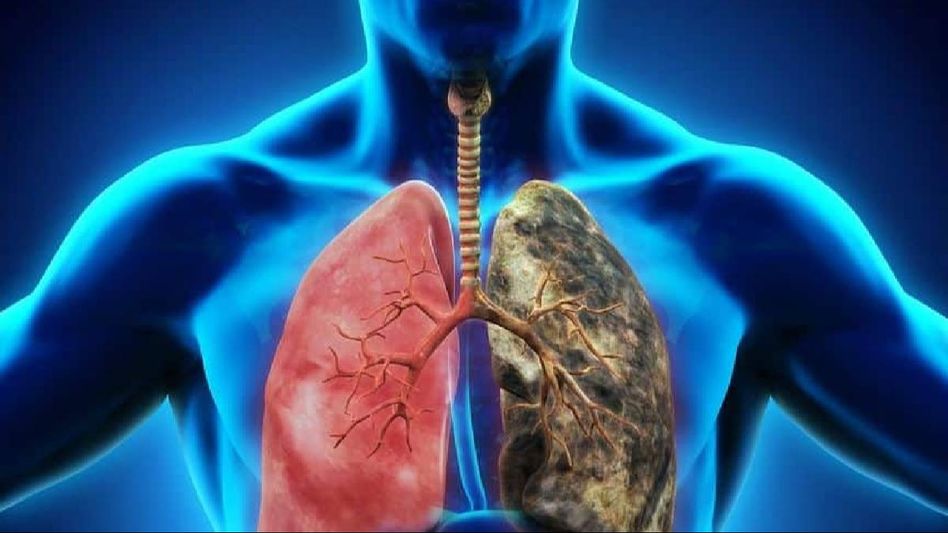
Respiratory diseases arise from various triggers, including environmental pollutants and genetic predispositions. Chronic exposure to tobacco smoke, both directly and indirectly, stands as a prominent risk factor, contributing significantly to the prevalence of conditions like COPD and lung cancer.
 Understanding Respiratory Diseases: Causes, Symptoms and Management
Understanding Respiratory Diseases: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementRespiratory diseases encompass a broad spectrum of conditions affecting the airways and lungs, significantly impacting human respiration. These ailments may stem from infections, tobacco smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, environmental pollutants such as radon and asbestos, among other factors. With diverse manifestations ranging from asthma to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), understanding the intricacies of these disorders is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Causes and Pathophysiology
Respiratory diseases arise from various triggers, including environmental pollutants and genetic predispositions. Chronic exposure to tobacco smoke, both directly and indirectly, stands as a prominent risk factor, contributing significantly to the prevalence of conditions like COPD and lung cancer. Additionally, occupational hazards, such as exposure to dust and chemicals, pose substantial threats to respiratory health.
The respiratory system's vulnerability to diseases can be attributed to its direct interface with the external environment and its extensive capillary network, making it susceptible to inhaled pathogens and toxins. Moreover, allergic reactions and sensitivities further complicate respiratory function, underscoring the multifactorial nature of these disorders.
Common Respiratory Diseases
Among the myriad respiratory ailments, asthma and COPD emerge as prevalent and debilitating conditions worldwide. Asthma is characterized by recurrent episodes of breathlessness, wheezing, and chest tightness, often triggered by allergens or environmental irritants. In contrast, COPD, primarily caused by long-term exposure to harmful gases or particles, manifests as progressive airflow limitation and persistent respiratory symptoms.
Emphysema, a hallmark of COPD, involves the destruction of alveolar walls, diminishing the lungs' capacity for efficient gas exchange. This results in symptoms like shortness of breath, chronic cough, and wheezing, significantly impairing respiratory function and quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of respiratory diseases is pivotal for timely intervention and management. Persistent cough, especially when accompanied by sputum production or hemoptysis, warrants thorough evaluation, as it may signify underlying inflammatory or malignant conditions. Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, serves as another cardinal symptom, reflecting the progressive nature of respiratory ailments like emphysema and fibrosis.
Individuals experiencing exacerbations of asthma or COPD may present with acute episodes of wheezing, chest tightness, and increased respiratory effort, necessitating prompt medical attention. Moreover, awareness of environmental triggers and lifestyle factors is crucial for minimizing symptom exacerbation and optimizing respiratory health.
Management and Prevention
While chronic respiratory diseases pose significant challenges, effective management strategies can alleviate symptoms and enhance patients' quality of life. Pharmacological interventions, including bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, play a central role in controlling airway inflammation and improving respiratory function. Moreover, lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and environmental mitigation, are integral components of disease management and prevention.
Preventive measures, including vaccination against respiratory infections and avoidance of known triggers, are paramount for reducing disease burden and mitigating complications. Additionally, public health initiatives aimed at promoting respiratory health awareness and improving access to care are essential for combating the global prevalence of respiratory diseases.
Respiratory diseases encompass a diverse array of conditions with significant implications for public health and individual well-being. By elucidating the underlying causes, signs, and symptoms of these ailments, healthcare professionals can facilitate early diagnosis and implement targeted interventions to optimize patient outcomes. Through collaborative efforts in research, education, and policy advocacy, strides can be made towards achieving a world where respiratory health is prioritized, and all individuals can breathe freely.
Sources:
1. National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). Respiratory Disease. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/respiratory-disease
2. Britannica. (n.d.). Respiratory Disease. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/science/respiratory-disease
3. World Health Organization. (n.d.). Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/health-topics/chronic-respiratory-diseases#tab=tab_1
Copyright©2025 Living Media India Limited. For reprint rights: Syndications Today









